FortiADC Quick Start Guide with examples
- Introduction
- Initial Setup
- SLB Configuration
- Case 1: 2 HTTP port 80 real servers, Round-robin load balancing, HTTP Status healthcheck, Layer 7
- Case 2: Same servers as above, but in addition make vpn.yurisk.com available only in the hours 08:00-20:30 and make Health Checks check actual page on the web site
- Case 3: Same servers as above, but rewrite any Host header in the request to the correct one vpn.yurisk.com using Rewrite rule
- Case 4: 2 FTP servers, Round-robin load balancing, verify availability by downloading a file from the servers
- Case 5: 3 HTTP servers, 2 serving vpn.yurisk.com, and 1 serving oldvpn.yurisk.com at the same WAN IP of 10.100.102.123
- Debug and Verificaiton
Introduction
FortiADC (FAD) is a load balancer, either for incoming connecitons to the server farm, or outgoing connections to multiple ISPs. It comes in VM and appliance form. The modes of use are:
-
Server Load Balancing (SLB) - main use case. FAD sits between Internet and your server9s)/server farm and intercepts all incoming to the servers connections from remote clients (forward proxy), doing load balancing and various manipulations, then passing those connections further to the servers.
-
Link Load Balancing (LLB) - sits between LAN users and multiple ISP lines, load balancing outgoing from LAN to Internet connections between these ISP lines to provide bandwidth sharing, NAT, links usage optimization, cost optimization. In F5 it would be LTM.
-
Global Load Balancing (GLB) - used as an option with SLB. The FAD works as an authoritative DNS server for your domain zone(s), doing DNS resolving for clients on the Internet to a specific FAD out of many FADs in different physical locations.
Initial Setup
On first connect, FAD will present the 1st config Wizard, which can be skipped or used.
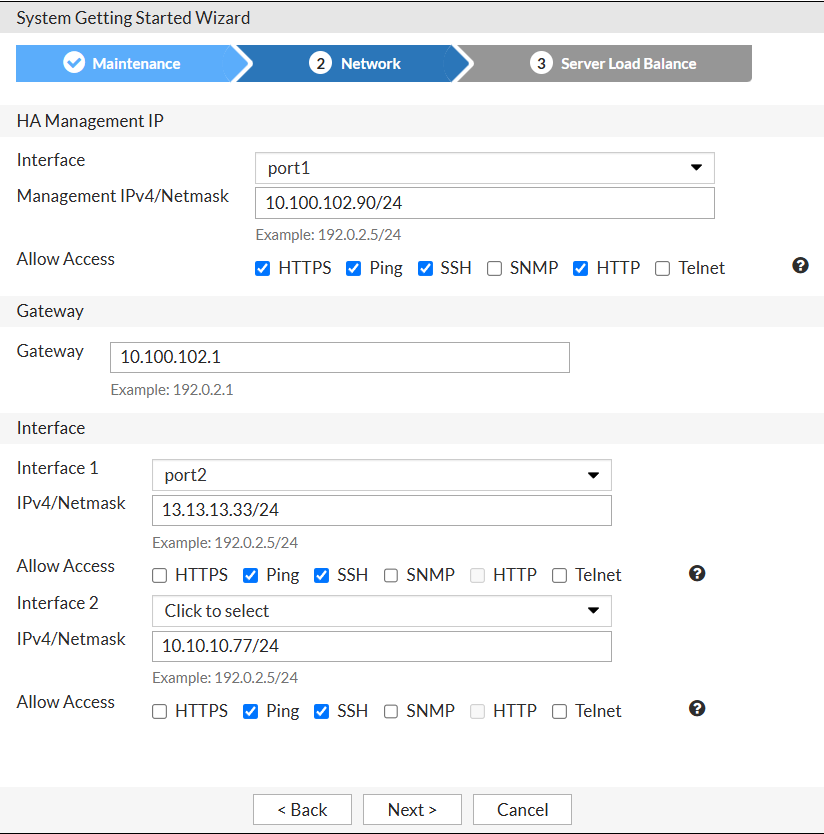
Just as Fortigate, FAD has local/remote admin accounts with access profiles, network interfaces with IPs (Network → Interface). All routing-related stuff goes to Network → Routing.
Admin access in FAD has 2 relevant configs: Trusted Host as usual per admin account, and Trust IP Address per interface. Source IP set per interface limits access of any admin account.
|
Note
|
I use the same interface (port1) for management and data traffic in this guide, but in production you should separate them as the best practice. |
SLB Configuration
The usual workflow:
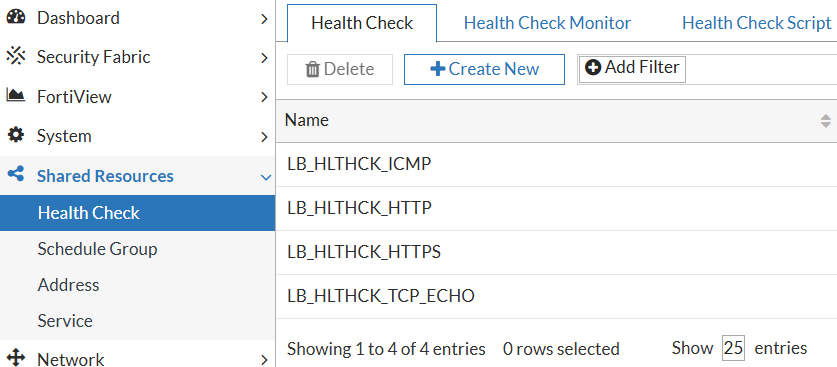
1) Configure custom Shared Resources or use the built-in. Mostly, you configure Health Checks here:
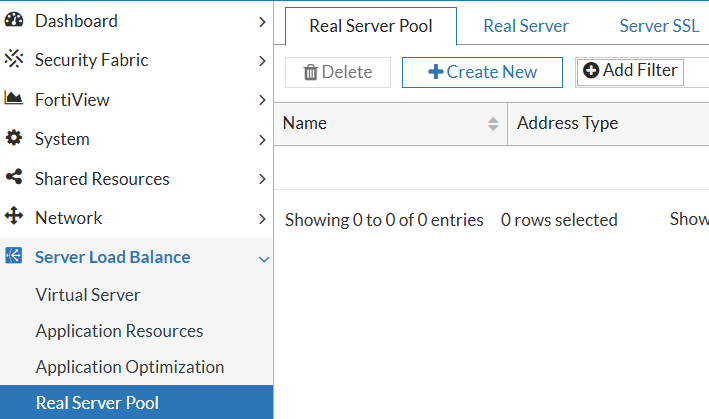
2) Configure Real Servers into server pool(s). I configure IPs, listening ports etc. of the real servers behind the FAD. You start creating a server pool, and inside it you create and add to the pool the real servers.
|
Note
|
In the whole workflow in FAD, it will show next steps in configuration only after you have saved the current step. Also, after creating some resource, you cannot change its name, only delete and re-create again. |
|
Note
|
Do not use dots in the resources names. |
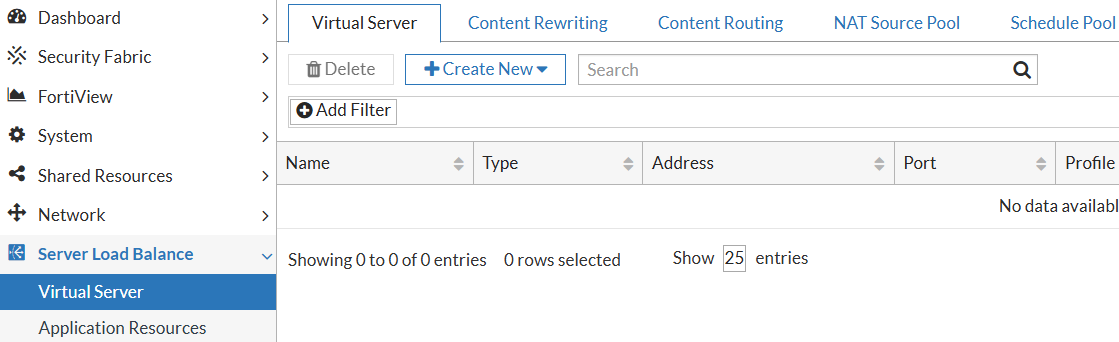
3) Create Virtual Server combining all the above, also configuring (optionally) Content Rewriting, Content Routing, NAT Source Pool, Schedule Pool.
Case 1: 2 HTTP port 80 real servers, Round-robin load balancing, HTTP Status healthcheck, Layer 7
Topology for this and further cases until said otherwise is:
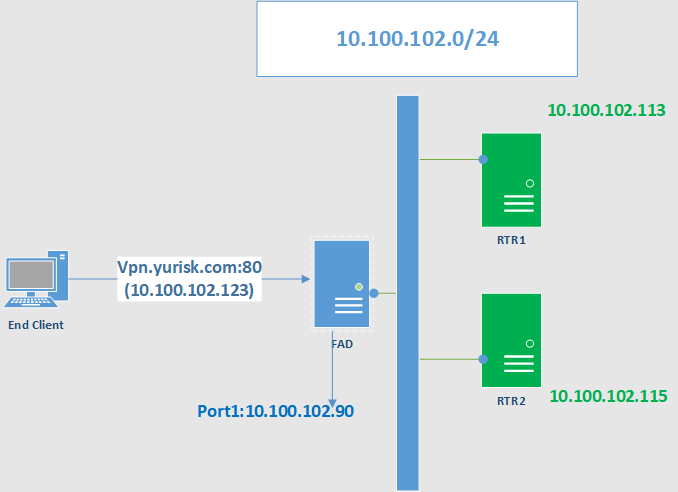
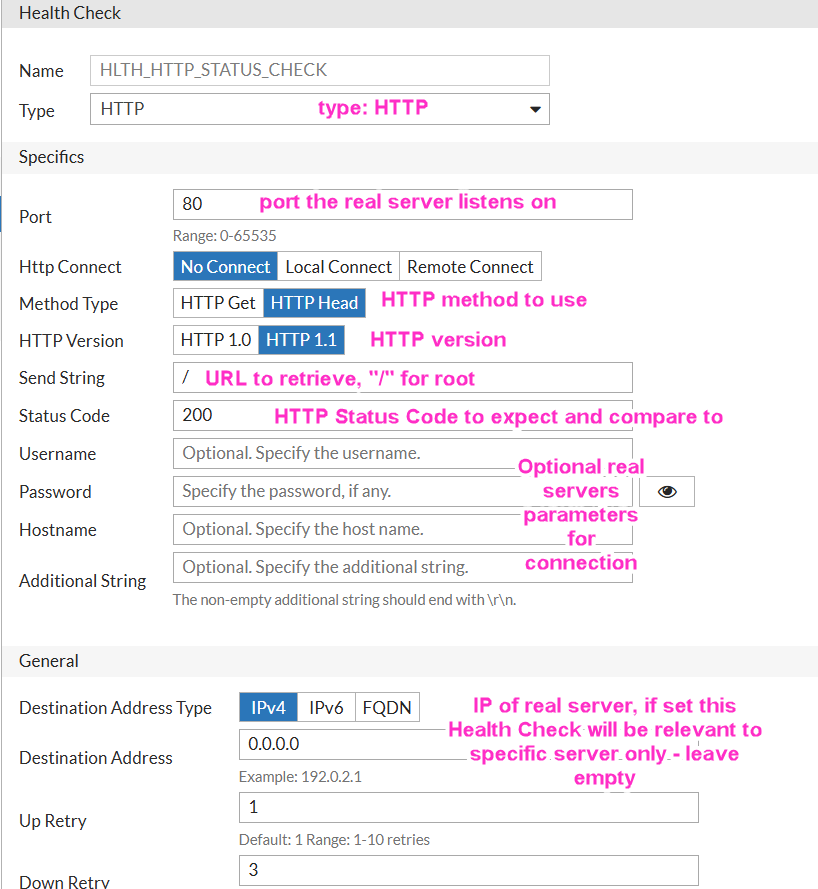
First are health checks. These will be HTTP real servers listening on port 80, so it is logical to check periodically connection to port 80 and issue HTTP HEAD command to get status as a reply, 200 (Success) being the expected one.
We do so in Shared Resources → Health Checks → New…
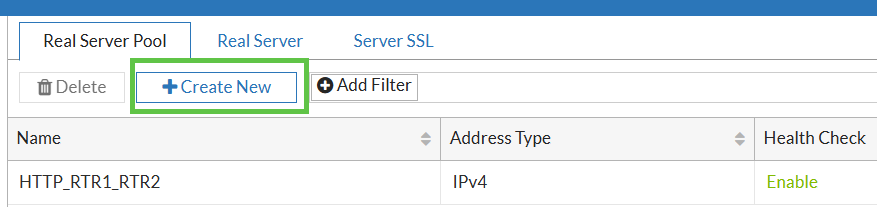
Next in Server Load Balance → Real Server Pool → Create New…
In new Real Server pool, we set IPv4, Static and Enable and the custom Health Check created above. After that we can add real servers, specifying for each its IP address, listening port, and leaving Health Check "Inherited" to be set for all real servers just once on the Real Server Pool level by clicking on member → Create New:
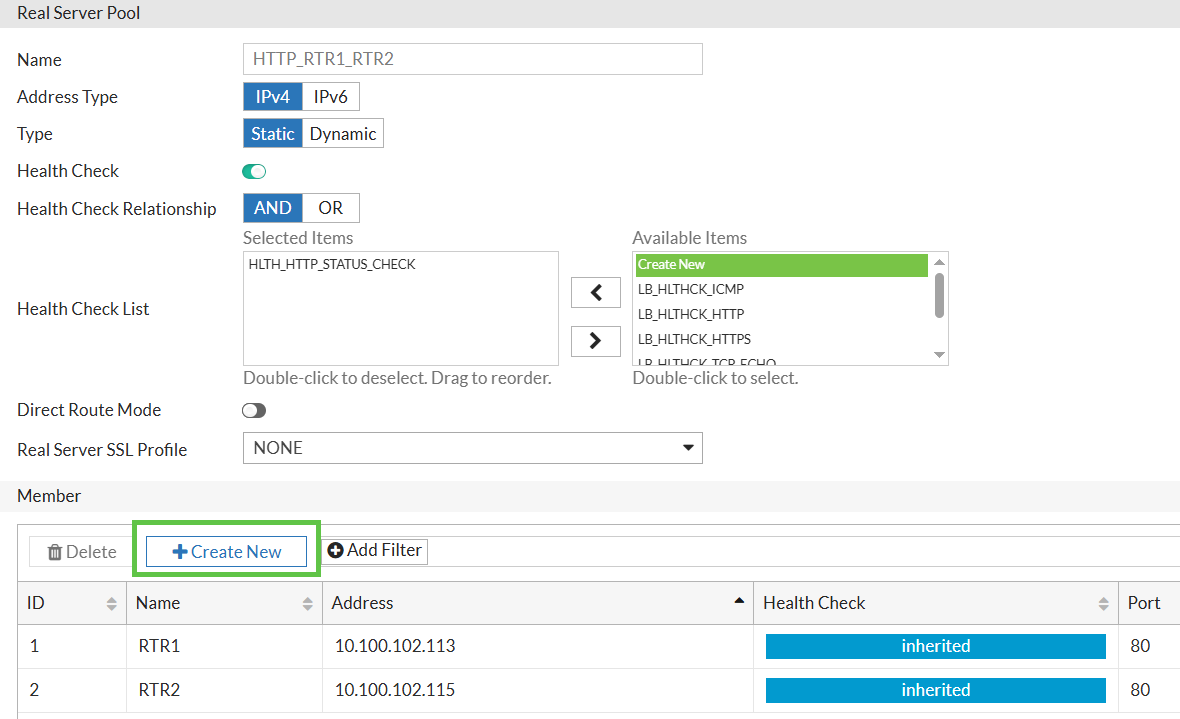
Example of settings for RTR1 real server:
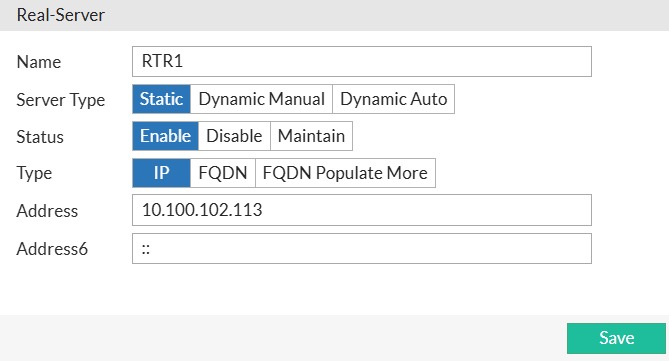
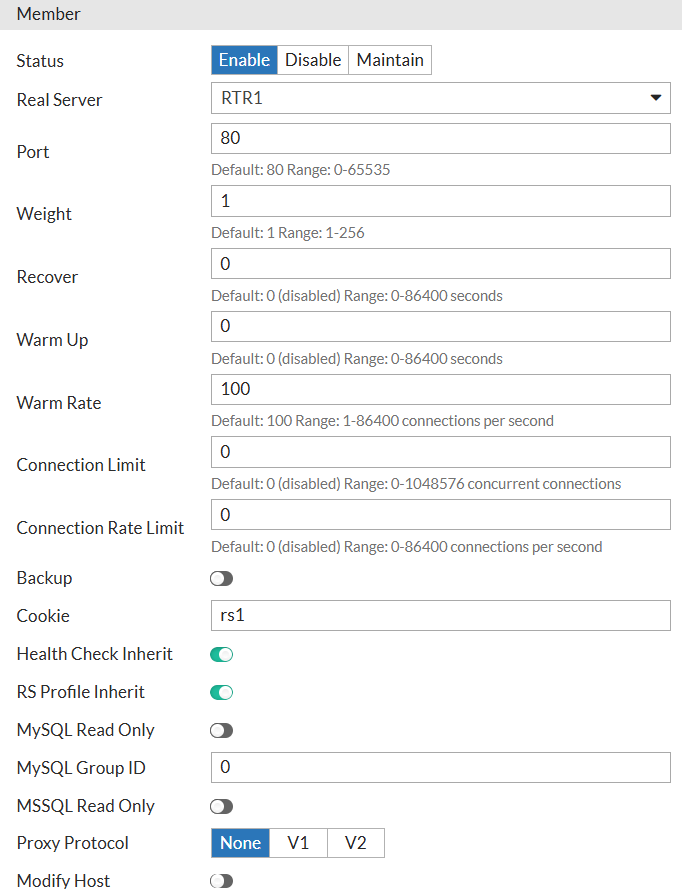
The final step is Virtual Server to tie together all the configs done so far.
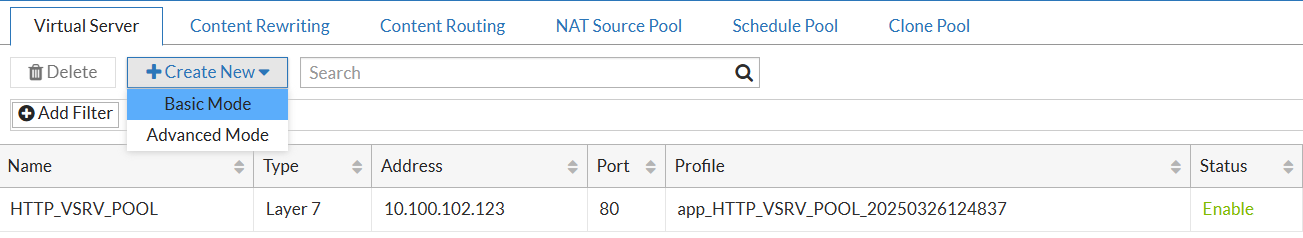
Server Load Balance → Create New → Basic/Advanced… the choice of Basic or Advanced is for initial wizard only, after the Virtual Server (vserver) has been created, editing it will have the same options. Here I pick Basic → HTTP:
Next, I set IP address for vserver - this is the IP seen by the end clients, and for which, for this case I created a domain record of vpn.yurisk.com that points to 10.100.102.123.
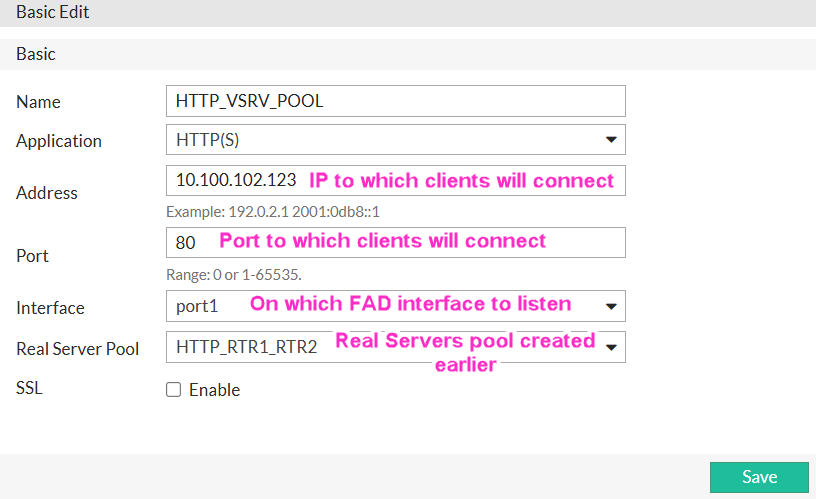
After saving, we got a whole lots of options 99% of which can be left on defaults:
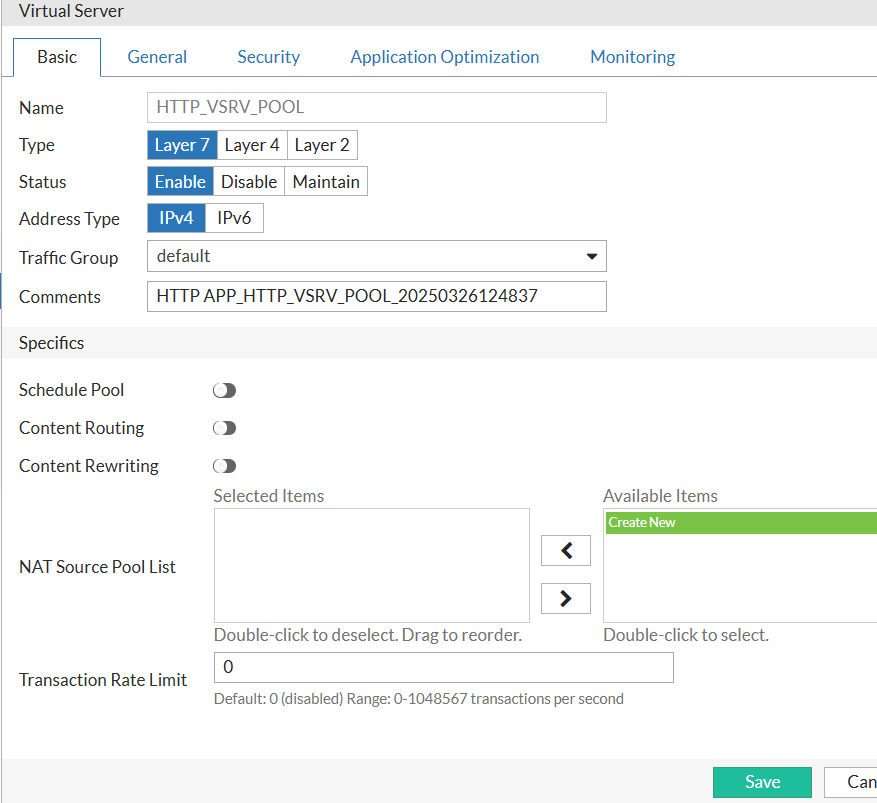
For this case, I will only pick the built-in Round-robin for the balancing method:
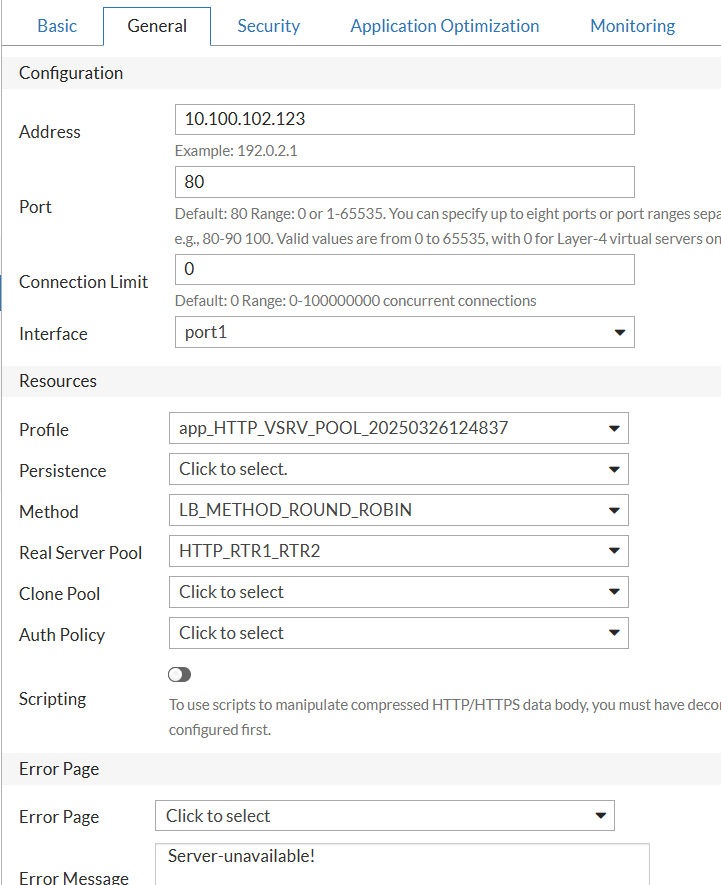
And will enable Traffic Logs for this vserver, be careful if doing this on production server as may overload the FAD with extensive logging:
Whole configuration on CLI
config router static
edit 1
set gateway 10.100.102.1
next
end
config system health-check
edit "HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK"
set type http
set port 80
next
end
config load-balance real-server
edit "RTR1"
set ip 10.100.102.113
next
edit "RTR2"
set ip 10.100.102.115
next
end
config load-balance pool
edit "HTTP_RTR1_RTR2"
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR1
next
edit 2
set pool_member_cookie rs2
set real-server RTR2
next
end
next
end
config load-balance method edit "app_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837" next end
config load-balance virtual-server
edit "HTTP_VSRV_POOL"
set type l7-load-balance
set interface port1
set ip 10.100.102.123
set load-balance-profile app_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837
set load-balance-method LB_METHOD_ROUND_ROBIN
set load-balance-pool HTTP_RTR1_RTR2
set traffic-log enable
set comments "HTTP APP_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837"
set traffic-group default
set fortiview enable
next
end
Verifying
On end client PC, trying vpn.yurisk.com in the browser gets me once to RTR1, once to RTR2 after few refreshes:
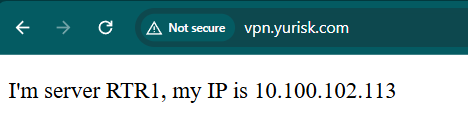
On the RTR2 server side, end client connection is seen with the source IP of 10.100.102.90 - IP set on port1 of the FAD and which FAD is using according to the route table when proxying incoming connection to the real server RTR2. The end client IP is 10.100.102.19 but real server does not see it:
rtr2# netstat -an -p tcp Active Internet connections (including servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address TCP-State tcp 0 0 10.100.102.115.80 10.100.102.90.47532 ESTABLISHED
On the real server RTR1, the sniffer shows health checks done by FAD - HEAD on port 80:
20:12:05.470475 10.100.102.90.50160 > 10.100.102.113.80 0000: 4500 00ae be30 4000 4006 9a86 0a64 665a E....0@.@....dfZ 0010: 0a64 6671 c3f0 0050 2ec8 db66 ad42 8fa2 .dfq...P...f.B.. 0020: 8018 003a 5fba 0000 0101 080a 5ca2 7cee ...:_.......\.|. 0030: f9eb 6437 4845 4144 202f 2048 5454 502f ..HEAD / HTTP/ 0040: 312e 310d 0a55 7365 722d 4167 656e 743a 1.1..User-Agent: 0050: 204b 6565 7041 6c69 7665 436c 6965 6e74 KeepAliveClient 0060: 0d0a 4361 6368 ..Cach
FAD is using strangely named User-Agent of KeepAliveClient.
Case 2: Same servers as above, but in addition make vpn.yurisk.com available only in the hours 08:00-20:30 and make Health Checks check actual page on the web site
When you hear time limitation - think Schedule, just as in Fortigate. So let’s create a schedule for 08:00-20:30.
Shared Resources → Schedule Group → New … After saving (basically just name) Schedule Group, you can add Member(s) - actual schedule(s).
I call the group DAY_HOURS, and inside it create a schedule named DAYS_HOURS_ONLY:
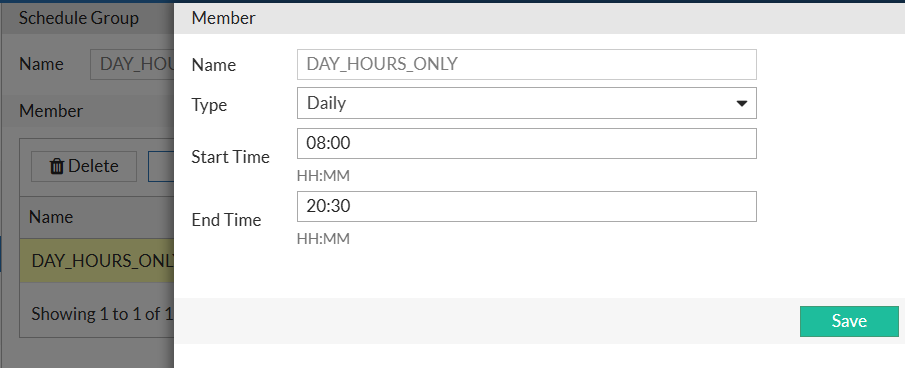
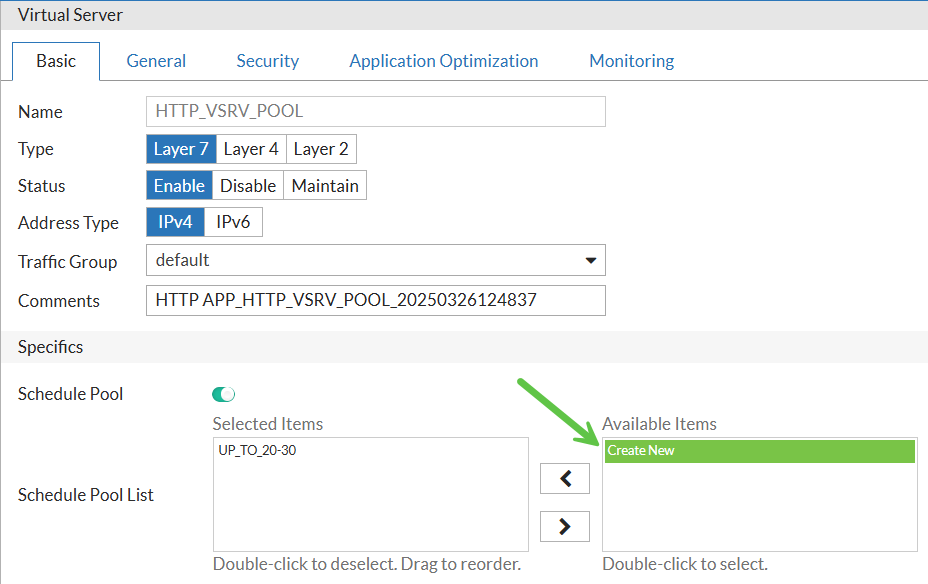
I go then to the vserver I created earlier, click on Edit and enable Schedule Pool, after which I double click on "Create New" and create new Schedule Pool named UP_TO_20-30 combining real servers pool with schedule group:
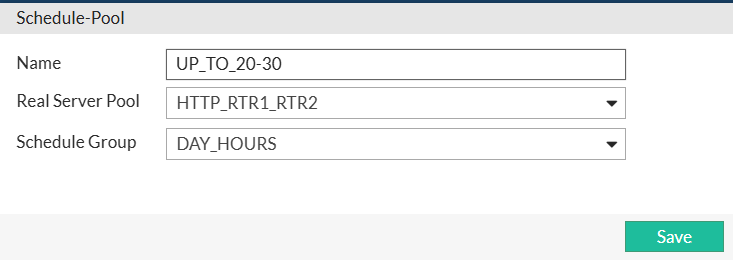
CLI configuration (only changes from above):
config system schedule-group
edit "DAY_HOURS"
config schedule-member
edit "DAY_HOURS_ONLY"
set type daily-recurring
set starttime-of-startdate 08:00
set endtime-of-enddate 20:30
next
end
next
end
config load-balance virtual-server
edit "HTTP_VSRV_POOL"
set type l7-load-balance
set interface port1
set ip 10.100.102.123
set load-balance-profile app_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837
set schedule-list enable <-- ENABLE SCHEDULE
set load-balance-method LB_METHOD_ROUND_ROBIN
set schedule-pool-list UP_TO_20-30 <-- SET SCHEDULE GROUP
set traffic-log enable
set comments "HTTP APP_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837"
set traffic-group default
set fortiview enable
next
end
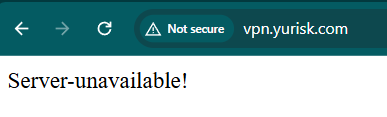
Verification. After the clock reaches 20:31 I try to enter the vpn.yurisk.com and instead of real server page, see the default error message:
Regarding the actual contents of a web page check - I created in each real server the page named monitor.html which is actually a text file that contains: on RTR1 the phrase "RTR1 All is good" and on RTR2 "RTR2 All is good". Then I configure 2 health checks for each router, as each router will present a different string in the page to match (for demonstration purposes only - I could put the same string to match in both servers' pages and then would only need 1 health check of both).
Health Check for RTR1:
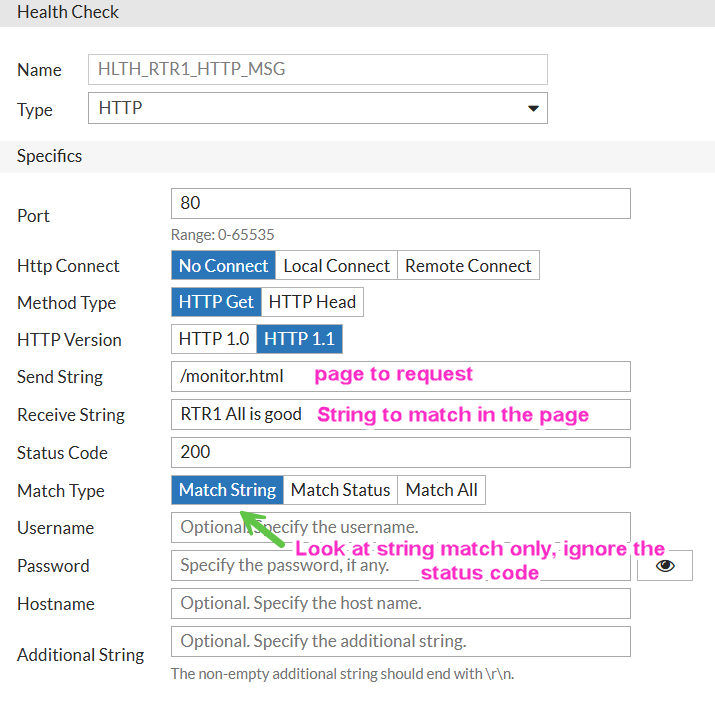
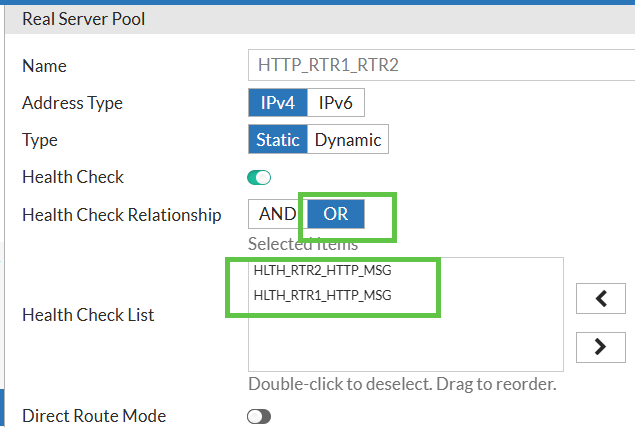
Using the health checks in the Real Server Pool - we have 2 options here, either put both checks at the pool level and change their Relationship from AND to OR, i.e. it will be enough for any of 2 checks to be successful. Or, more orderly, remove health check at pool level, and set them individually at each server level. I will do the 2nd option.
The 1st option - setting health check on Real Server Pool level would look like that:
For the set up I want, I will edit each real server under real servers pool, here is RTR1:
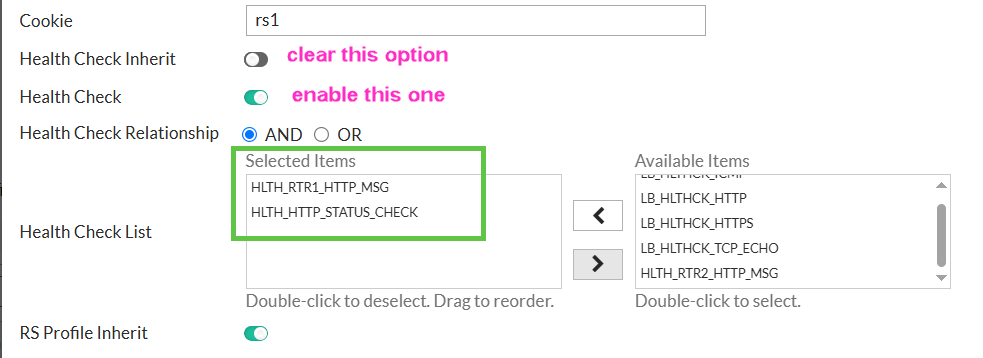
As you can see, I added 2 health checks - one checks contents of the returned page, second one checks that status is 200 (OK), even though I could check status inside the 1st, page checking monitor.
I do the same for the RTR2:
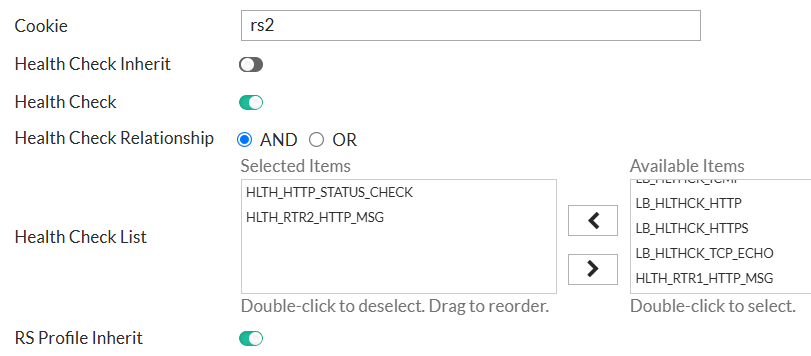
And will remove the health check at the real server pool level:
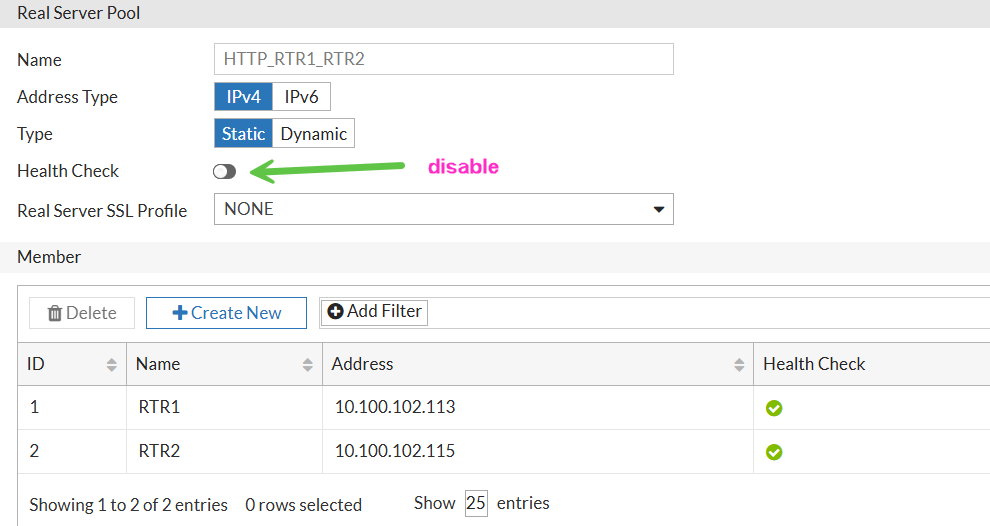
CLI Configuration (only changes):
config system health-check
edit "HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK"
set type http
set port 80
next
edit "HLTH_RTR1_HTTP_MSG"
set type http
set port 80
set method-type http_get
set send-string /monitor.html
set receive-string "RTR1 All is good"
next
edit "HLTH_RTR2_HTTP_MSG"
set type http
set port 80
set method-type http_get
set send-string /monitor.html
set receive-string "RTR2 All is good"
set match-type match_all
next
end
config load-balance pool
edit "HTTP_RTR1_RTR2"
set health-check-list HLTH_RTR2_HTTP_MSG HLTH_RTR1_HTTP_MSG
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set health-check-inherit disable
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_RTR1_HTTP_MSG HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR1
next
edit 2
set health-check-inherit disable
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK HLTH_RTR2_HTTP_MSG
set pool_member_cookie rs2
set real-server RTR2
next
end
next
end
For verification I will shut down RTR1, the health checks changes to warning and RTR1 is removed from active servers:
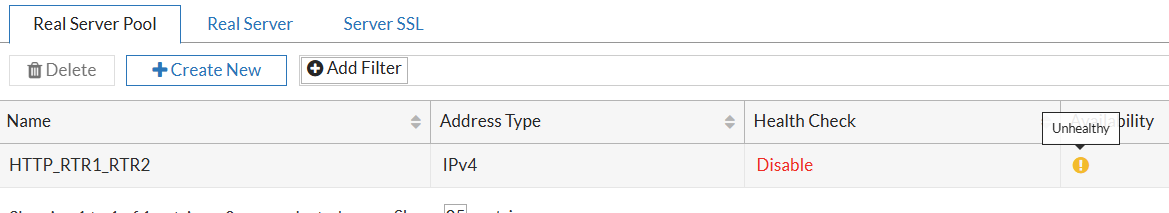
Case 3: Same servers as above, but rewrite any Host header in the request to the correct one vpn.yurisk.com using Rewrite rule
When switching old subdomains to new locations, you usually set up a DNS redirect via a CNAME record to point to the new name/location. However, the client’s browser will still be using the old Host header. For example, if you had oldvpn.yurisk.com hosting your website and moved it to vpn.yurisk.com, browsers with oldvpn.yurisk.com configured will continue sending oldvpn.yurisk.com as the Host header value even to the new location. And if the new webserver does not recognize this domain, it will return an Error 404 "Not Found".
To prevent this, we can create Content Rewriting (applicable to HTTP only) rule for all incoming HTTP requests for their Host header to be re-written to the correct vpn.yurisk.com in each client’s request.
You do so in the Server Load Balance → Virtual Server → Content Rewriting → New… by creating a new Rewrite rule(s), and then attaching it inside the Virtual Server config. The matching can be either string or regex, I will use regex here that will match any value of Host header:
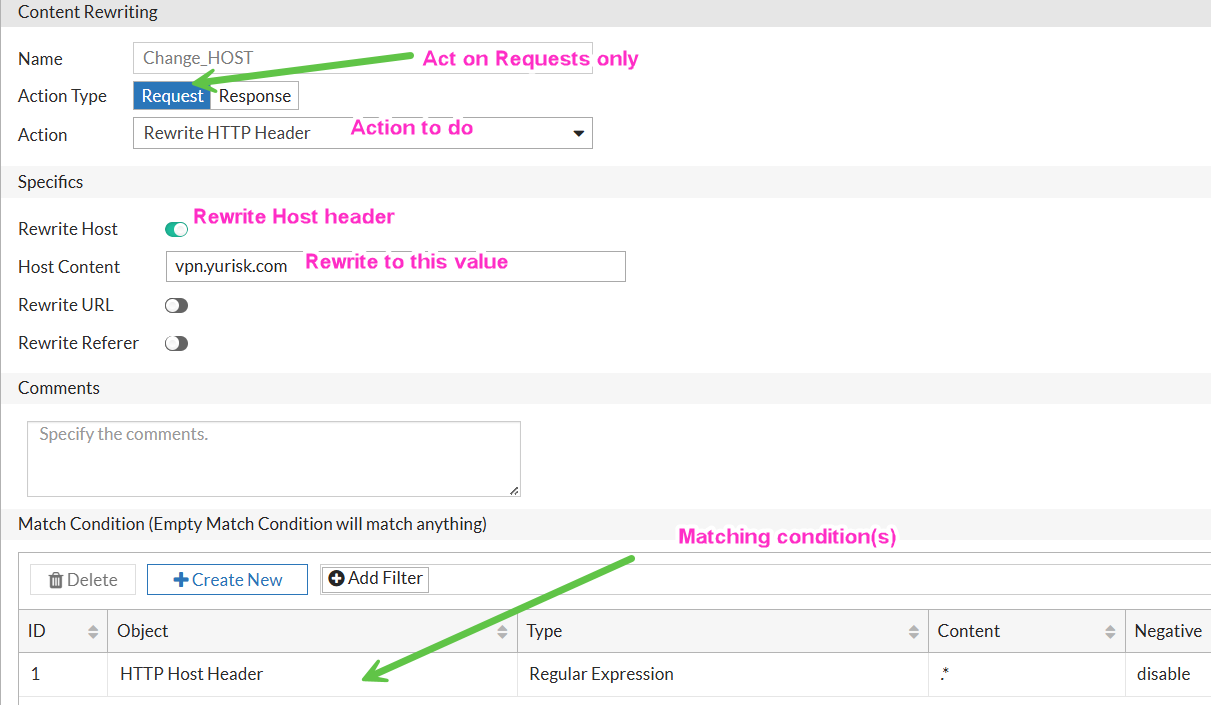
Now attach it to the vserver:
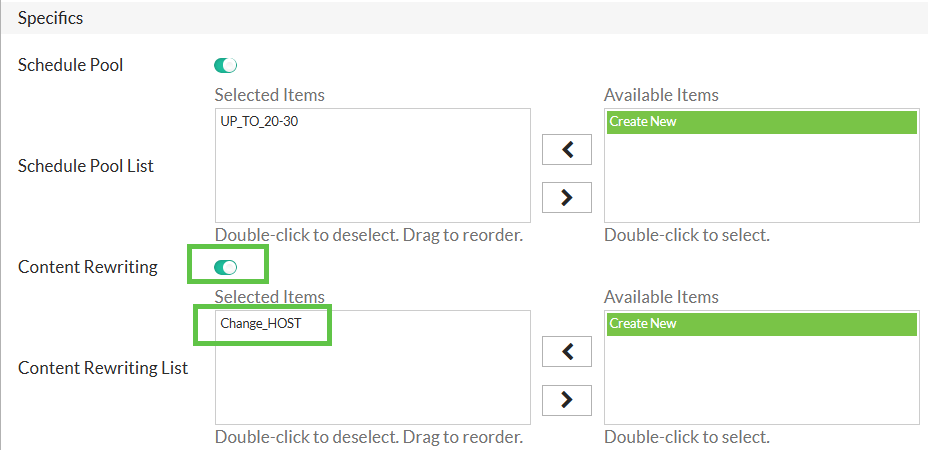
CLI Configuration.
config load-balance content-rewriting
edit "Change_HOST"
set action rewrite_http_header
set host-status enable
set host vpn.yurisk.com
config match-condition
edit 1
set type regular-expression
set content .*
next
end
next
end
config load-balance virtual-server
edit "HTTP_VSRV_POOL"
set type l7-load-balance
set interface port1
set ip 10.100.102.123
set load-balance-profile LB_PROF_HTTP
set content-rewriting enable
set content-rewriting-list Change_HOST <-- THE RULE
set schedule-list enable
set load-balance-method LB_METHOD_ROUND_ROBIN
set schedule-pool-list UP_TO_20-30
set traffic-log enable
set comments "HTTP APP_HTTP_VSRV_POOL_20250326124837"
set traffic-group default
set fortiview enable
next
end
Verification Doing sniffer on FAD, I can see that HTTP request comes from end client for the Host of oldvpn.yurisk.com but then is replaced with vpn.yurisk.com when exits the FAD to the real server (RTR2 here). Client IP is 10.100.102.5:
port1 in 10.100.102.5.59364 -> 10.100.102.123.80 ..GET./.HTTP/1.1 ..Host:.oldvpn.yurisk.com.. <-- ORIGINAL Upgrade-Insecure-Requests:.1..Accept: .text/html,application/xhtml+xml ,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 ..User-Agent:.Mozilla/5.0.(Macin tosh;.Intel.Mac.OS.X.10_15_7).Ap pleWebKit/605.1.15.(KHTML,.like. Gecko).Version
port1 out 10.100.102.90.34082 -> 10.100.102.115.80 .+GET./.HTTP/1.1 ..Host:.vpn.yurisk.com.. <-- REWRITTEN HOST Upgrade-Insecure-Request s:.1..Accept:.text/html,applicat ion/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q= 0.9,*/*;q=0.8..User-Agent:.Mozil la/5.0.(Macintosh;.Intel.Mac.OS. X.10_15_7).AppleWebKit/605.1.15. (KHTML,.like.Gecko).Version/17
Case 4: 2 FTP servers, Round-robin load balancing, verify availability by downloading a file from the servers
The finished logical diagram will be seen in FortiView → Logical Topology:

I’ll start the same way as with HTTP - create Health Check for FTP.
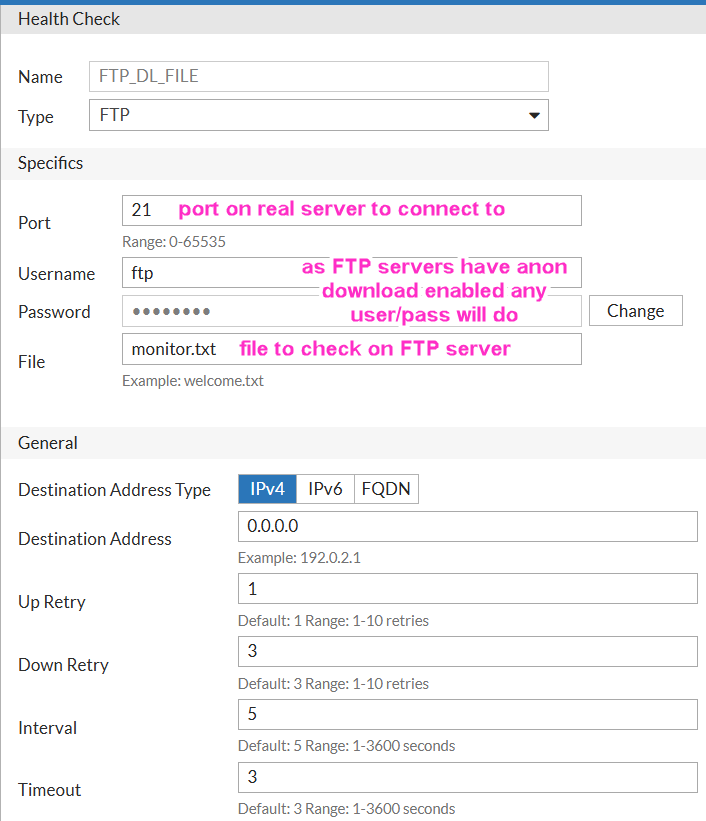
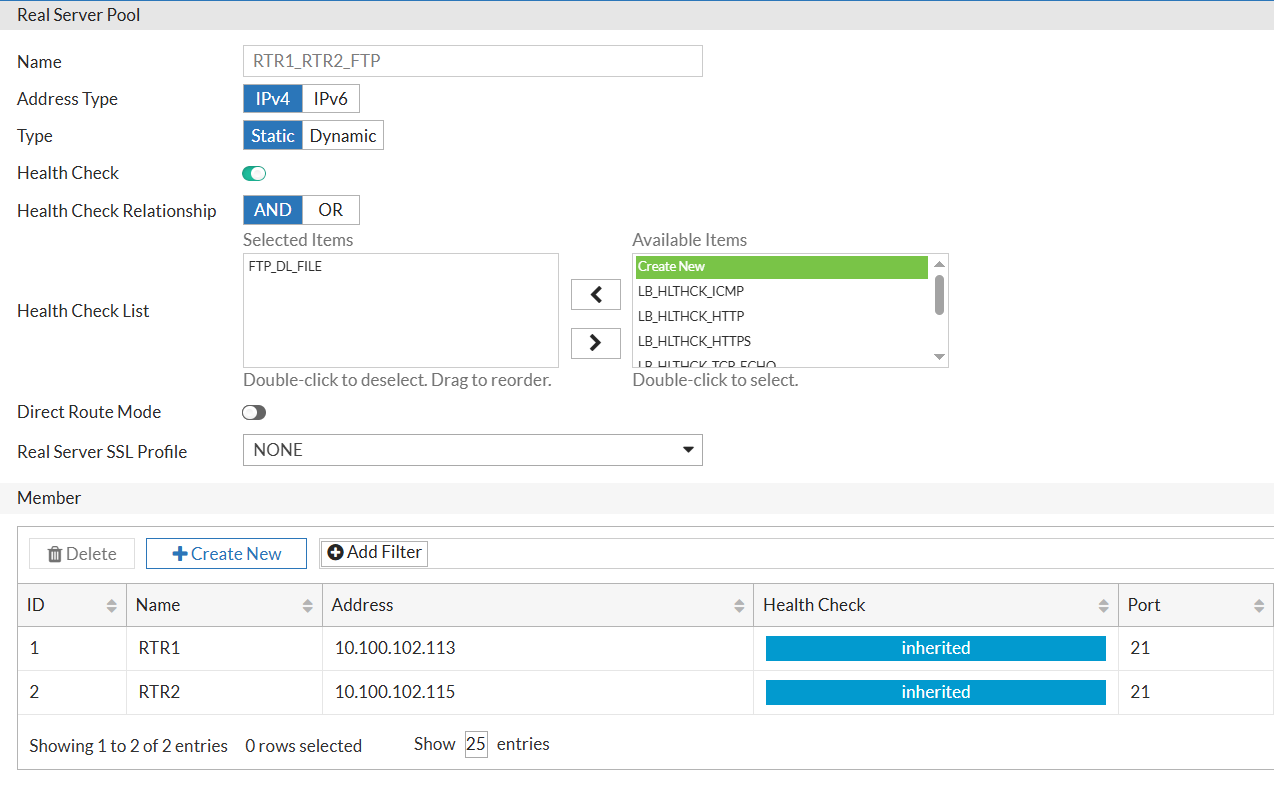
Then I create a Real Server Pool with 2 FTP servers, and add the Health Check to it.
Here, RTR1 - 10.100.102.113, RTR2 - 10.100.102.115. I will use the same Health Check for both servers, as file name to check monitor.txt is the same on both servers. I will use the default FTP port 21.
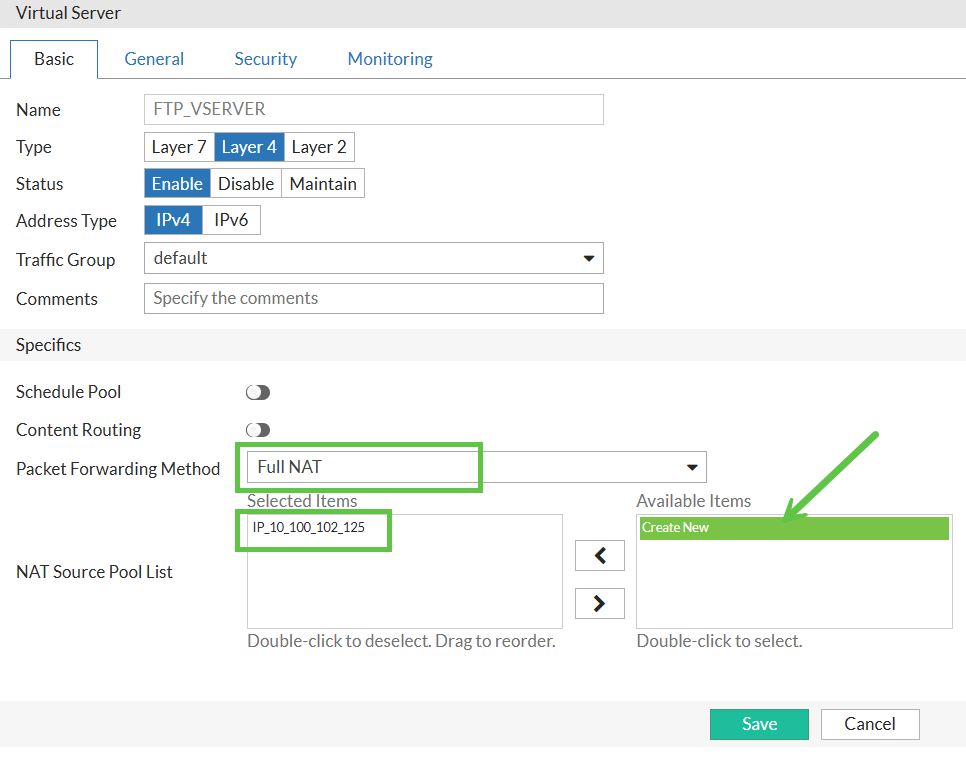
And, finally, the Virtual Server. It will be different from the HTTP one in that I will create Layer 4 vserver, as FortiADC only supports Layer 7 for HTTP and HTTPS. I will use the default FTP port 21, and will set the load balancing method to Round Robin. Also, I will have to create and use Full NAT as forwarding method, as Layer 4 vserver does not act as full Layer 7 proxy, and does not change the source IP of the client to the FAD IP. This is important for FTP, as FTP uses 2 connections - control and data, and the data connection is opened by the server to the client, so if the client IP is not changed to FAD IP, the server will try to connect back to the client IP directly, bypassing the FAD, which will not work.
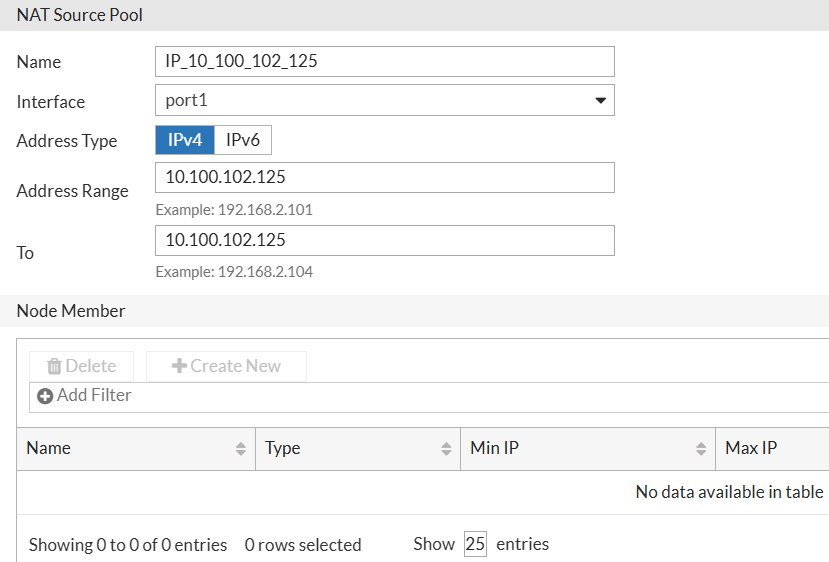
NAT Source Pool used in Vserver:
In General properties I set the Round-robin algo:
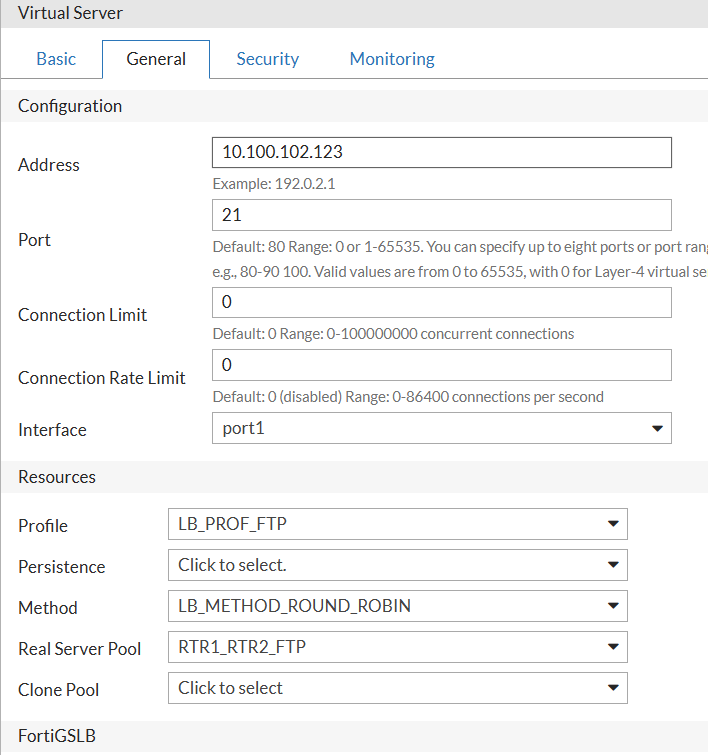
-
CLI Configuration
config system health-check
edit "FTP_DL_FILE"
set type ftp
set port 21
set username ftp
set password ENC rhwXABt
set file monitor.txt
next
end
config load-balance ippool
edit "IP_10_100_102_125"
set interface port1
set ip-min 10.100.102.125
set ip-max 10.100.102.125
config node-member
end
next
end
config load-balance real-server
edit "RTR1"
set ip 10.100.102.113
next
edit "RTR2"
set ip 10.100.102.115
next
end
config load-balance pool
edit "RTR1_RTR2_FTP"
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list FTP_DL_FILE
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set pool_member_service_port 21
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR1
next
edit 2
set pool_member_service_port 21
set pool_member_cookie rs2
set real-server RTR2
next
end
next
end
config load-balance virtual-server
edit "FTP_VSERVER"
set packet-forwarding-method FullNAT
set interface port1
set ip 10.100.102.123
set port 21
set load-balance-profile LB_PROF_FTP
set load-balance-method LB_METHOD_ROUND_ROBIN
set load-balance-pool RTR1_RTR2_FTP
set ippool-list IP_10_100_102_125
set traffic-group default
next
end
Verification The active connecitons can be seen in FortiView → All Sessions:
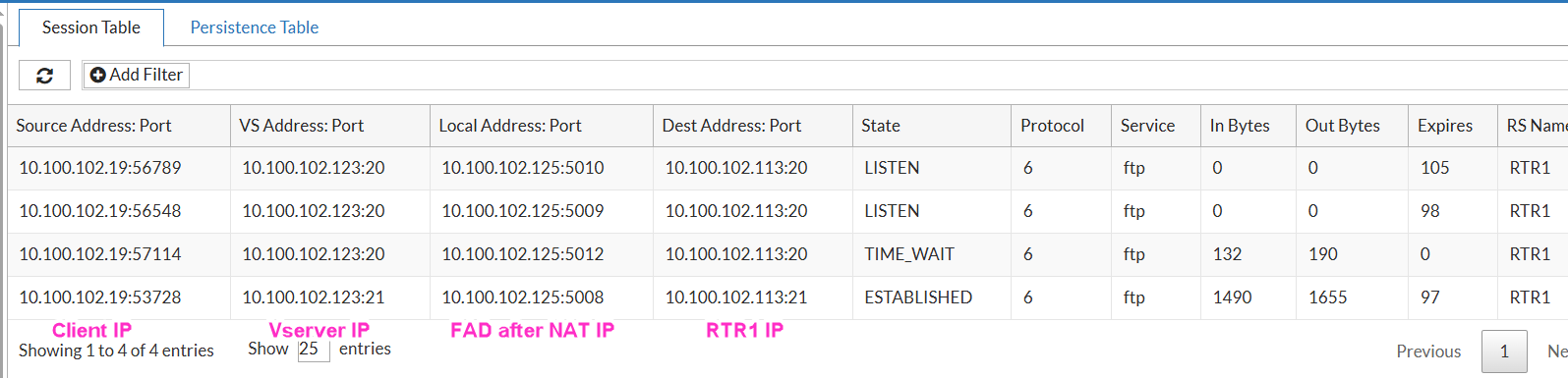
Here, the client to FTP connection is to port 21, and FTP server to client data transfer connection is sourced from port 20 on the server.
Case 5: 3 HTTP servers, 2 serving vpn.yurisk.com, and 1 serving oldvpn.yurisk.com at the same WAN IP of 10.100.102.123
When serving multiple domains on the same WAN IP (here 10.100.102.123) but using different real servers for each domain, FortiADC’s Content Routing will be the one to use. It routes requests to real servers based on Layer 4 or Layer 7 info. For subdomains, Layer 7 is used to route based on the Host header. Thus, oldvpn.yurisk.com is routed to RTR3 (10.100.102.117), while vpn.yurisk.com is routed to RTR1 and RTR2.
The finished Logical Topology can be seen in FortiView → Logical Topology:

-
Create Health Check. I will use created earlier
HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECKfor all 3 servers, as it is checking the status of the server by issuing HTTP HEAD command to port 80. -
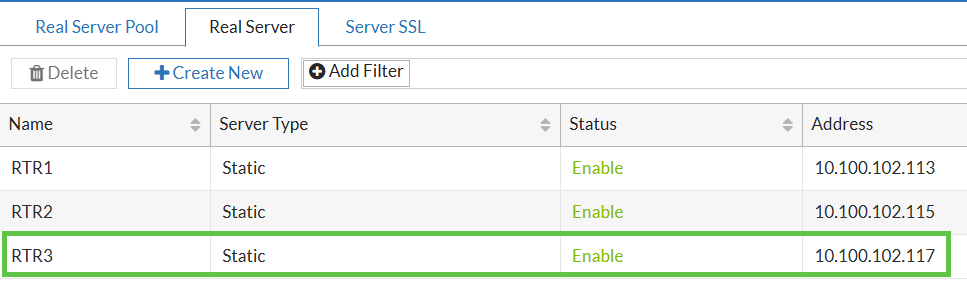
Create all Real Servers. I already have RTR1 & RTR2 from previous cases serving subdomain
vpn.yurisk.com, now I will add RTR3 the same way as the previous 2 to serveoldvpn.yurisk.com.
The final table or Real Servers will look:
-
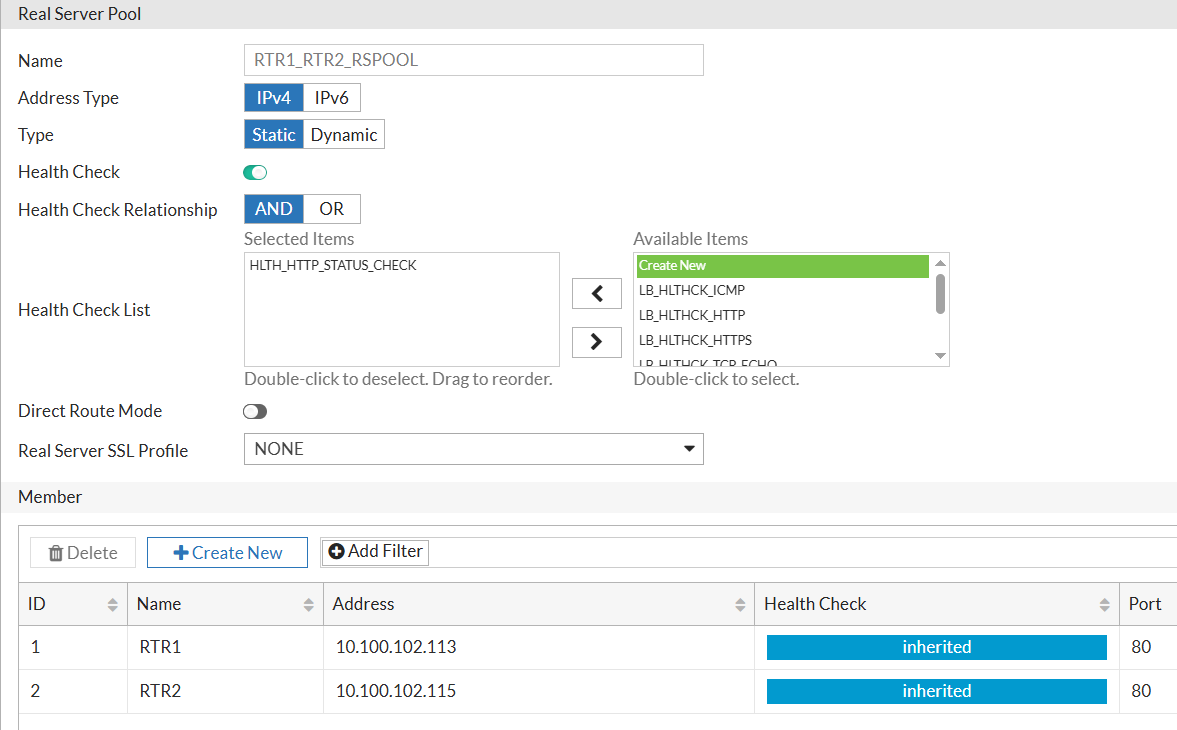
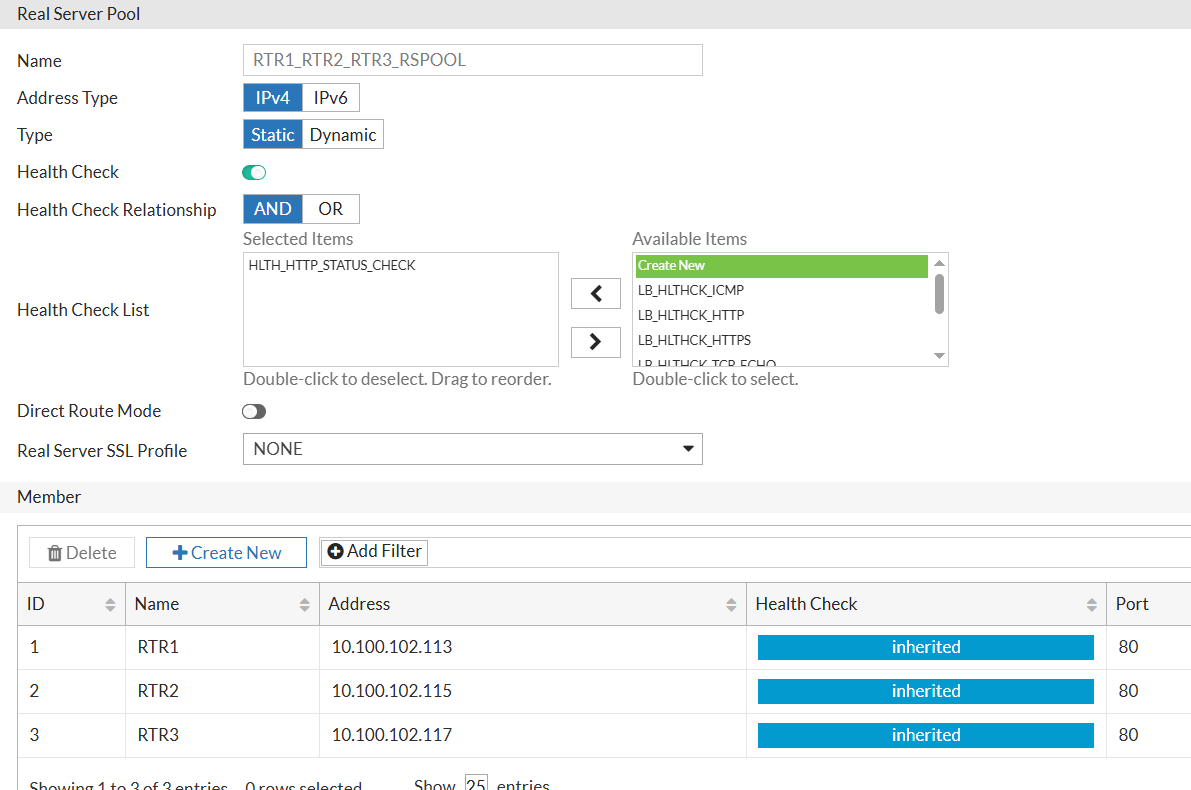
Create Real Servers Pool. I will create 3 pools - one for RTR1 and RTR2, one for RTR3, and one including all 3 servers. The first pool will be used for
vpn.yurisk.com, the second foroldvpn.yurisk.com, and the third one will be the fallback, used for all 3 servers in case of failure.
RTR1 & RTR2 Pool:
RTR3 Pool:
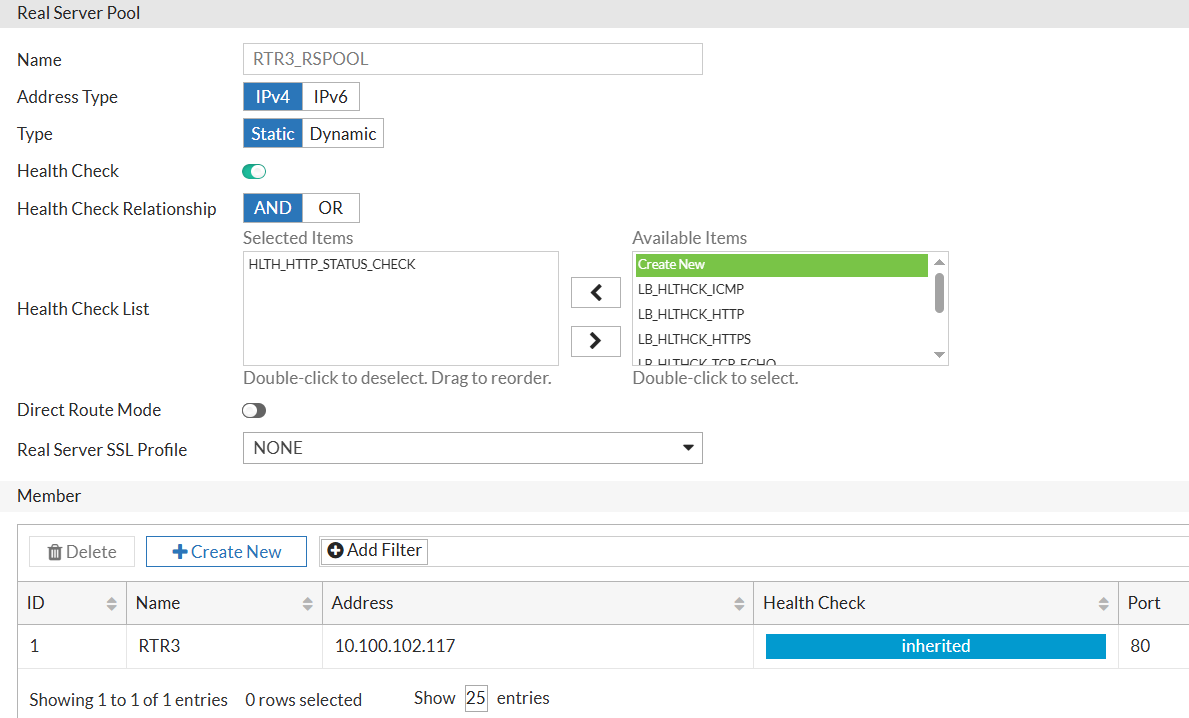
RTR1, RTR2, and RTR3 Pool (will be assigned at Vserver level, will be used if the first 2 pools fail):
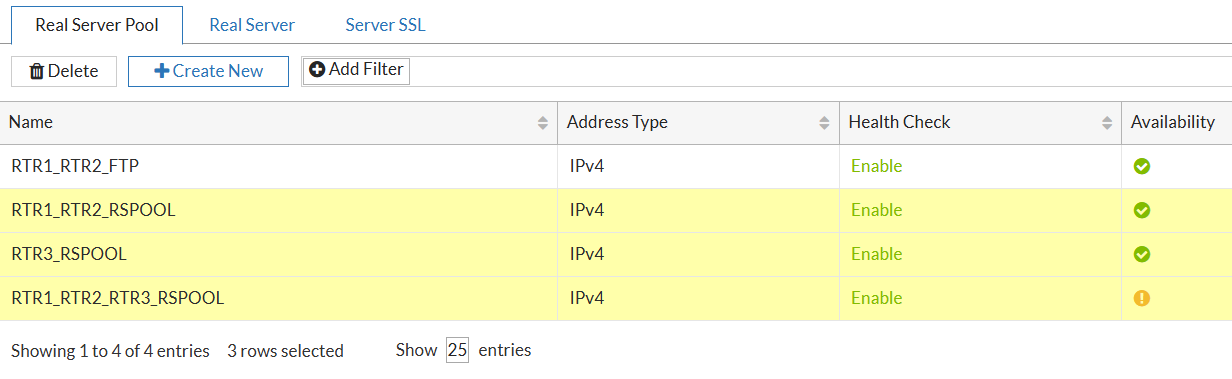
Final look of all Real Servers Pools:
-
Now, the main part - create Content Routing rules. I will create 2 rules - one for
vpn.yurisk.comand one foroldvpn.yurisk.com. The first rule will match the Host header ofvpn.yurisk.comand route it to the RTR1 & RTR2 pool, while the second rule will match the Host header ofoldvpn.yurisk.comand route it to the RTR3 pool.
Rule for vpn.yurisk.com matching the Host header via regex:
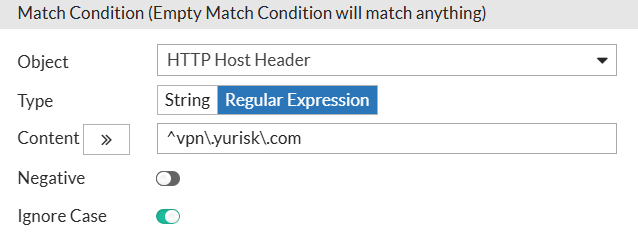
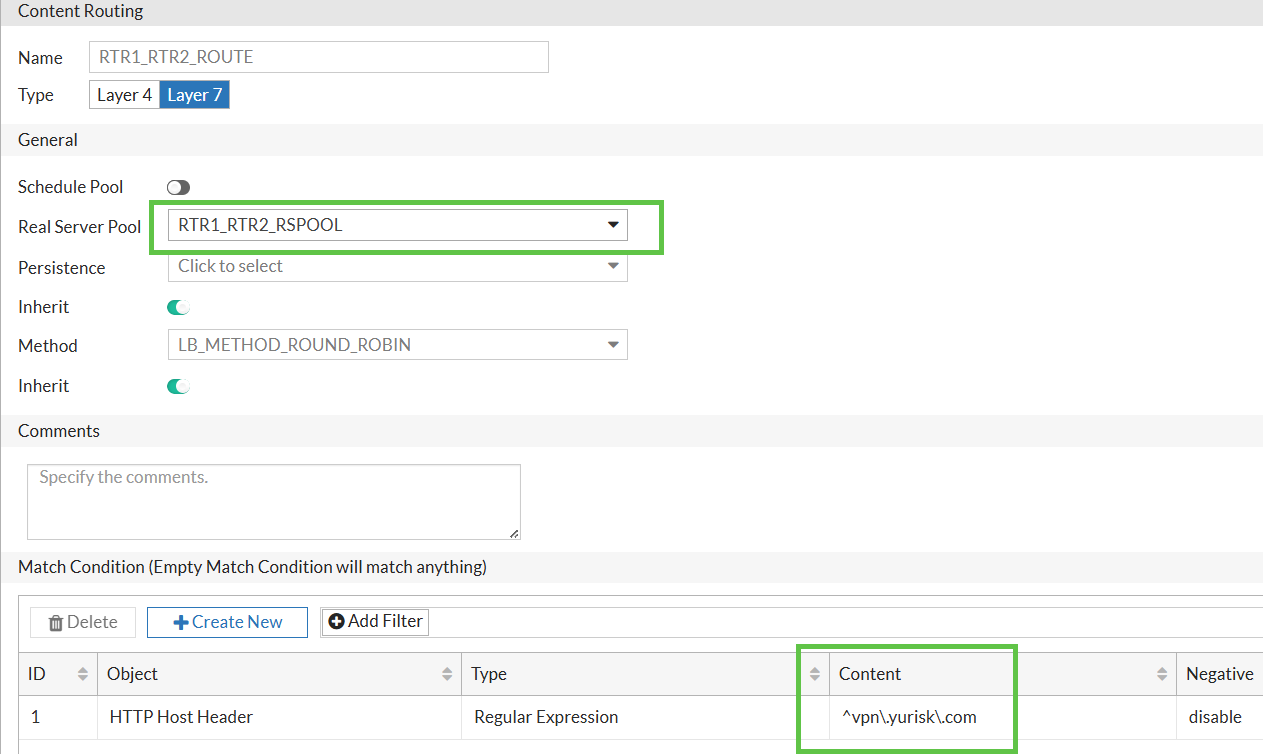
Rule for oldvpn.yurisk.com:
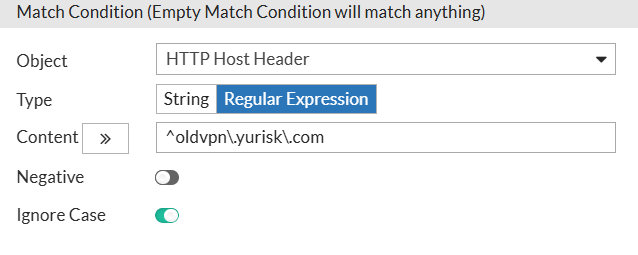
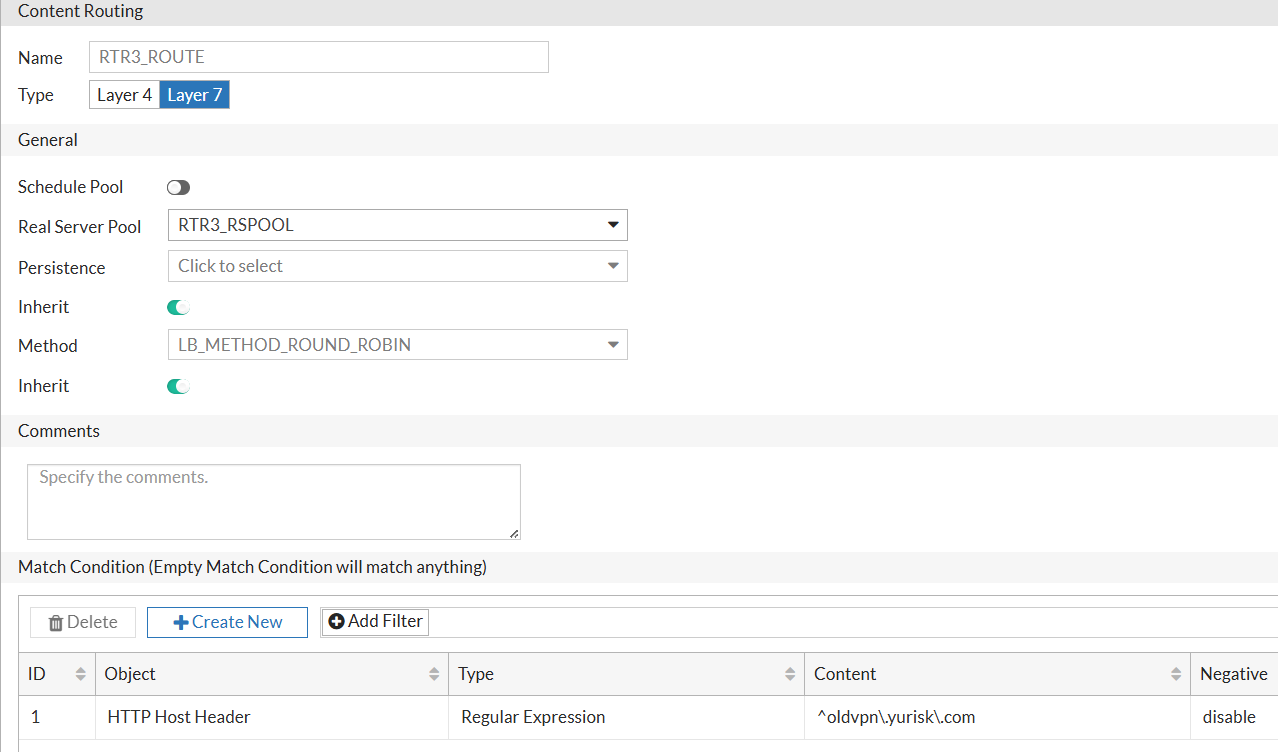
Final look of Content Routing rules:
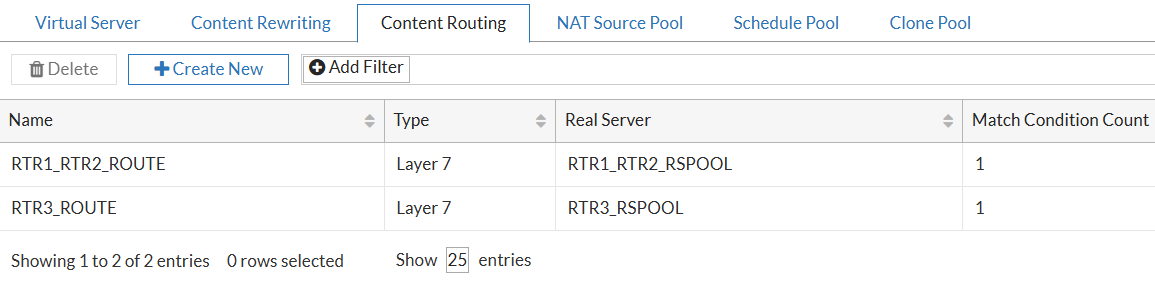
Finally, I will combine all the above into the Virtual Server. Not seen here, but when creating the vserver, I have to specify the default/fallback pool (the one with all 3 servers) in the Real Servers Pool field. I cannot leave it empty. But the Content Routing rules, which I enable and specify, will be used to route the traffic to the correct pool based on the Host header as they have precedence over the default Server Pool.
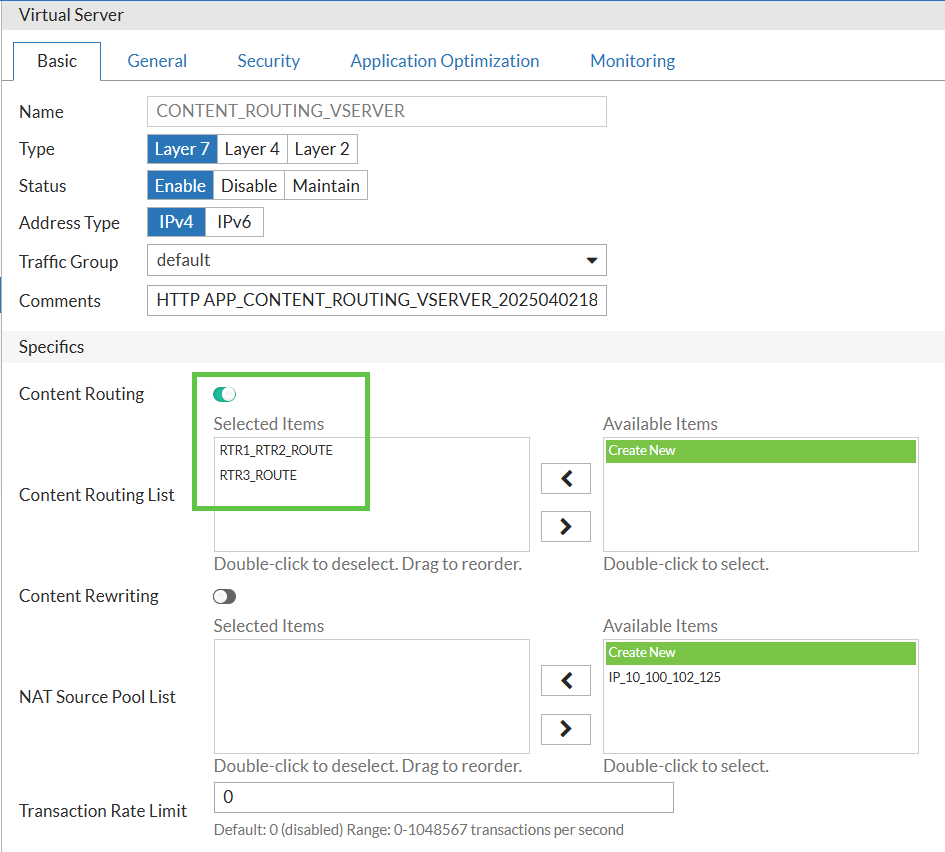
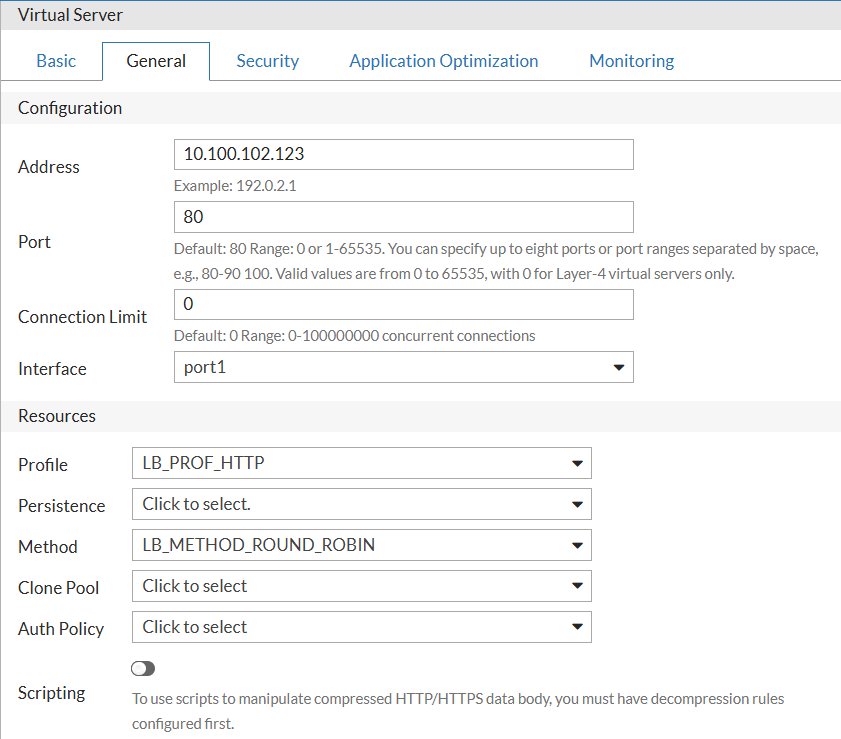
Verification
I will try to enter from the same client PC 10.100.102.19 to both web pages - oldvpn.yurisk.com and vpn.yurisk.com. The first one will be routed to RTR3, the second one to RTR1 or RTR2.
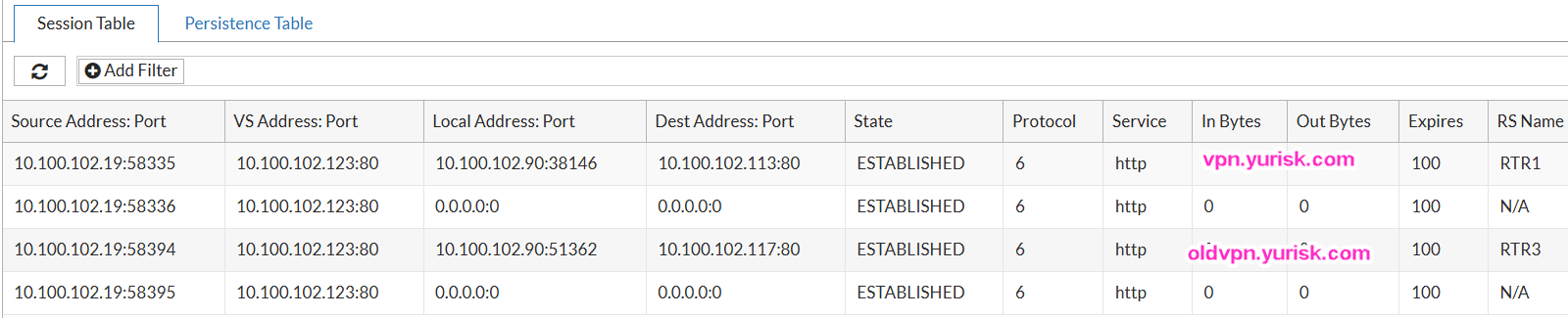
-
CLI Configuraiton
config system health-check
edit "HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK"
set type http
set port 80
next
end
config load-balance profile
edit "app_CONTENT_ROUTING_VSERVER_20250402185619"
set type http
next
end
config load-balance real-server
edit "RTR1"
set ip 10.100.102.113
next
edit "RTR2"
set ip 10.100.102.115
next
edit "RTR3"
set ip 10.100.102.117
next
end
config load-balance pool
edit "RTR1_RTR2_RSPOOL"
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR1
next
edit 2
set pool_member_cookie rs2
set real-server RTR2
next
end
next
edit "RTR3_RSPOOL"
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR3
next
end
next
edit "RTR1_RTR2_RTR3_RSPOOL"
set health-check-ctrl enable
set health-check-list HLTH_HTTP_STATUS_CHECK
set real-server-ssl-profile NONE
config pool_member
edit 1
set pool_member_cookie rs1
set real-server RTR1
next
edit 2
set pool_member_cookie rs2
set real-server RTR2
next
edit 3
set pool_member_cookie rs3
set real-server RTR3
next
end
next
end
config load-balance method edit "app_CONTENT_ROUTING_VSERVER_20250402185619" next end
config load-balance content-routing
edit "RTR1_RTR2_ROUTE"
set load-balance-pool RTR1_RTR2_RSPOOL
config match-condition
edit 1
set type regular-expression
set content "^vpn\\.yurisk\\.com"
next
end
next
edit "RTR3_ROUTE"
set load-balance-pool RTR3_RSPOOL
config match-condition
edit 1
set type regular-expression
set content "^oldvpn\\.yurisk\\.com"
next
end
next
end
config load-balance virtual-server
edit "CONTENT_ROUTING_VSERVER"
set type l7-load-balance
set interface port1
set ip 10.100.102.123
set load-balance-profile LB_PROF_HTTP
set content-routing enable
set content-routing-list RTR1_RTR2_ROUTE RTR3_ROUTE
set load-balance-method LB_METHOD_ROUND_ROBIN
set comments "HTTP APP_CONTENT_ROUTING_VSERVER_20250402185619"
set traffic-group default
next
end
Debug and Verificaiton
-
get system perf Show general load on the FAD:
FortiADC-VM # get sys performance CPU usage: 0% used, 100% idle Memory usage: 16% used System Load: 0 Uptime: 3 days 0 hours 14 minutes
-
The usual diagnose sys top works as well.
FortiADC-VM # diagnose system top Mem: 2767204K used, 13527476K free, 4303094K shrd, 14588K buff, 1163640K cached CPU: 0.0% usr 0.0% sys 0.0% nic 100% idle 0.0% io 0.0% irq 0.0% sirq Load average: 0.71 0.35 0.28 1/256 19168 PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %VSZ CPU %CPU COMMAND 2464 1 root S 1440m 9.0 0 0.0 /bin/adfsproxy 2460 1 root S 1418m 8.8 0 0.0 /bin/ocgs 4305 1 root S 1369m 8.5 0 0.0 /bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/my.cnf --skip-grant-tables --ski 2492 1 root S 1114m 6.9 0 0.0 /bin/restapi 2 2491 1 root S 1110m 6.9 0 0.0 /bin/restapi 1 2488 1 root S 928m 5.8 0 0.0 /bin/ptd 2437 1 root S 726m 4.5 0 0.0 /bin/alertd 2778 1 root S 644m 4.0 0 0.0 /bin/infod 2461 1 root S 626m 3.9 0 0.0 /bin/hasyncd -CUT-
-
Sometimes, it is worth increasing Logs verbosity: Log & Report → Logs Settings
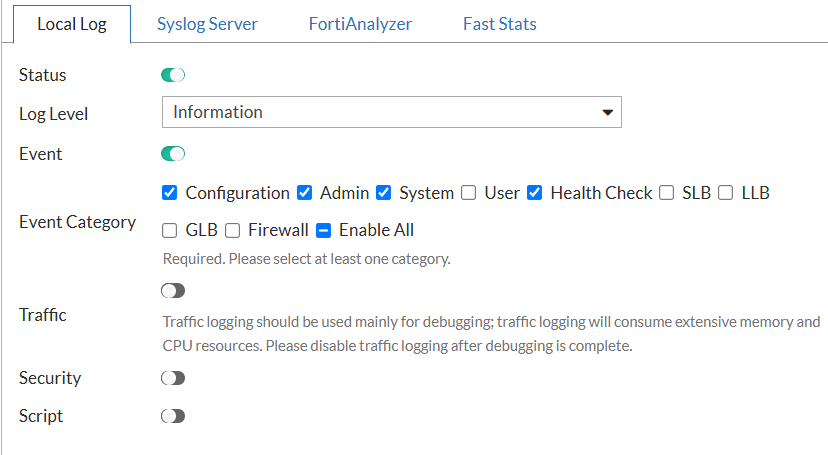
-
Debug of a specific FAD module is done with diagnose debug module <name> all, dia deb enable.
FortiADC-VM # diagnose debug module adfs set/get debug level for AD FS daemon alertd set/get debug level for alert events and metric apisecd set/get debug level for apisecd authd set/get debug level for authd av set/get debug level for anti-virus daemon awsd set/get debug level for awsd bfd set/get debug level for bfd daemon bgpd set/get debug level for bgpd daemon cm_client set/get debug level for cm_client daemon cmdb set/get debug level for CLI and CMDB cmdb_event set/get debug level for cmdb event crlupdated set/get debug level for crlupdated daemon dnsd set/get debug level for dnsd dnsproxy set/get debug level for dnsproxy daemon fast_statis set/get debug level for fast_statis events fcnacd set/get debug level for fcnacd flg_accessd set/get debug level for flg_accessd daemon flg_indexd set/get debug level for flg_indexd daemon flg_reportd set/get debug level for flg_reportd daemon fnginx set/get debug level for fnginx daemon forticldd set/get debug level for forticldd daemon gdns set/get debug level for gdns daemon -CUT-
-
Show VM license status dia deb vm-license:
FortiADC-VM # dia deb vm-license Serial-Number: FADV0000000TRIAL License info : Trial License is in use.(Expire in 11 days 20 hours 57 mins) License CPU : 0 Contract CPU : 0
-
For TAC cases, you may gather all the logs/configs/current stats in System → Debug → Save Debug File.
-
The common exe ping, exe traceroute, exe reboot are available as well.
-
And, of course, the sniffer we know from Fortigate is here too: diagnose sniffer packet:
diagnose sniffer packet any 'port 443'
interfaces=[any]
filters=[port 443]
5.440606 port1 in 10.100.102.19.50110 -> 10.100.102.90.443:
psh 3293991010 ack 2459888613
0x0000 0000 0000 0001 b42e 990e 3ea5 0800 4500
0x0010 0347 7843 4000 8006 9e38 0a64 6613 0a64
0x0020 665a c3be 01bb c456 5062 929e ebe5 5018
0x0030 2012 b05c 0000 1703 0303 1a00 0000 0000
-
Show used disk space diag hardware get sysinfo df or fnsysctl df -h:
diag hardware get sysinfo df FortiADC-VM # diag hardware get sysinfo df Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 674.7M 498.0M 162.6M 75% / none 0 0 0 0% /proc none 0 0 0 0% /sys none 0 0 0 0% /sys/kernel/debug none 512.0M 31.0M 481.0M 6% /tmp none 0 0 0 0% /dev/pts none 512.0M 390.2M 121.8M 76% /dev/shm none 256.0M 0 256.0M 0% /tmp2 none 512.0M 17.3M 494.7M 3% /tmp3 none 128.0M 16.5M 111.5M 13% /tmp_hc_root none 560.0M 4.0K 560.0M 0% /tmp_av cgroup 7.8G 0 7.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup cgroup 0 0 0 0% /sys/fs/cgroup/memory cgroup 0 0 0 0% /sys/fs/cgroup/tmpfs_control /dev/sda1 183.6M 149.7M 24.1M 86% /data /dev/sdb1 29.4G 422.1M 27.4G 1% /var/log /dev/sda3 368.3M 76.6M 272.1M 22% /home /dev/sdb1 29.4G 422.1M 27.4G 1% /var/log /dev/sda3 368.3M 76.6M 272.1M 22% /home none 512.0M 0 512.0M 0% /var/ps_cache none 0 0 0 0% /proc tracefs 0 0 0 0% /sys/kernel/debug/tracing
-
Show active settings for an interface get system interface [name]
FortiADC-VM # get system interface port1 type : physical dedicate-to-mgmt : disable mode : dhcp vdom : root redundant-master : ip : 10.100.102.90/24 allowaccess : https ping ssh http mtu : 1500 speed : auto status : up retrieve_physical_hwaddr : disable mac-addr : 00:0c:29:64:1e:2b flow-sniffer : disable retrieve_dhcp_gateway : disable wccp : disable trust-ip : disable recv-seg-offload-override : disable send-seg-offload-override : disable
-
Errors and such on the interfaces diagnose hardware get deviceinfo nic-detail:
FortiADC-VM # diagnose hardware get deviceinfo nic-detail
Interface: port1
driver: vmxnet3
version: 1.4.a.0-k-NAPI
firmware-version:
expansion-rom-version:
bus-info: 0000:03:00.0
supports-statistics: yes
supports-test: no
supports-eeprom-access: no
supports-register-dump: yes
supports-priv-flags: no
Settings for port1:
Supported ports: [ TP ]
Supported link modes: 1000baseT/Full
10000baseT/Full
Supported pause frame use: No
Supports auto-negotiation: No
Supported FEC modes: Not reported
Advertised link modes: Not reported
Advertised pause frame use: No
Advertised auto-negotiation: No
Advertised FEC modes: Not reported
Speed: 10000Mb/s
Duplex: Full
Port: Twisted Pair
PHYAD: 0
Transceiver: internal
Auto-negotiation: off
MDI-X: Unknown
Supports Wake-on: uag
Wake-on: d
Link detected: yes
Inter-| Receive
face |bytes packets errs drop fifo frame compressed multicast
port1: 19336081 187098 0 0 0 0 0
2228 85240755 69852 0 0 0 0 0 0
-
Show all configured IPs on FAD interfaces dia netlink ip list:
FortiADC-VM # diagnose netlink ip list IP=127.0.0.1 MASK=255.255.255.0 index=1 devname=lo IP=127.129.1.1 MASK=255.255.255.255 index=1 devname=lo IP=10.100.102.90 MASK=255.255.255.0 index=4 devname=port1 IP=13.13.13.33 MASK=255.255.255.0 index=7 devname=port2 IP=169.254.30.43 MASK=255.255.0.0 index=19 devname=haport0
-
Show ARP table diagnose netlink neighbor list:
FortiADC-VM # diagnose netlink neighbor list Address Age(min) Hardware Addr Interface 10.100.102.1 21 21:3f:1c:06:f8:57 port1 10.100.102.19 4237 b4:2e:99:0e:3e:a5 port1
-
Show routing table get router info routing-table all:
FortiADC-VM # get router info routing-table all
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, O - OSPF, B - BGP
P - PPPoE, i - isp, D - dhcp, > - selected route, * - FIB route
S>* 0.0.0.0/0 [10/0] via 10.100.102.1, port1
C>* 10.100.102.0/24 is directly connected, port1
C>* 13.13.13.0/24 is directly connected, port2
C>* 169.254.0.0/16 is directly connected, haport0
-
Show kernel boot messages: fn dmesg.
-
Show daemons crash logs (if there were crashes): diagnose crashlog list.
I also write cheat sheets/scripts/guides to help in daily work, so make sure to check out my Github at https://github.com/yuriskinfo and https://www.linkedin.com/in/yurislobodyanyuk/